本文共 16864 字,大约阅读时间需要 56 分钟。
文章目录
开篇
接上个部分讲到了客户端发送请求的过程,这个部分我们分析服务端接收请求并发送响应的过程。
在分析的过程中,provider启动netty服务端的时候(NettyServer.doOpen),会在在ChannelPipeline链中加入了4个ChannelHandler。
- NettyCodecAdapter.InternalEncoder:编码器- NettyCodecAdapter.InternalDecoder:解码器- IdleStateHandler:心跳处理器- NettyServerHandler:请求处理器
- 在服务端接收客户端响应时,首先会经过解码器NettyCodecAdapter.InternalDecoder,然后经过NettyServerHandler.channelRead进行请求处理。
- 服务端接收请求处理之后,接着响应结果客户端,经过NettyServerHandler.write进行结果响应,然后经过NettyCodecAdapter.InternalEncoder编码器进行编码处理,最终响应给客户端。
接下来们将其拆分为处理请求和响应结果进行分析。
处理客户端请求
解码过程
解码过程不做具体分析
NettyCodecAdapter.InternalDecoder.decode-->DubboCountCodec.decode -->ExchangeCodec.decode -->DubboCodec.decodeBody
经过解码得到请求对象Request。
读取请求过程
1. NettyServerHandler.channelRead
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler); try { handler.received(channel, msg); } finally { NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ctx.channel()); } } 2. AbstractPeer.received
装饰角色,维护了closed状态
public void received(Channel ch, Object msg) throws RemotingException { // 如果通道已经关闭,则直接返回 if (closed) { return; } handler.received(ch, msg);} 3. MultiMessageHandler.received
对多消息的处理。
@Override public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { //如果消息是MultiMessage类型的,做下类型转换 if (message instanceof MultiMessage) { MultiMessage list = (MultiMessage) message; 遍历发送 for (Object obj : list) { handler.received(channel, obj); } } else { handler.received(channel, message); } } 4. HeartbeatHandler.received
对心跳事件做了处理。
如果不是心跳请求,那么接下去走到AllChannelHandler的received。否则直接回复响应,不再继续往下走。public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { setReadTimestamp(channel); //是否属于心跳的请求 if (isHeartbeatRequest(message)) { Request req = (Request) message; if (req.isTwoWay()) { Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion()); res.setEvent(Response.HEARTBEAT_EVENT); channel.send(res); } return; } //是否属于心跳的响应 if (isHeartbeatResponse(message)) { return; } handler.received(channel, message); } 5. AllChannelHandler.received
这里io事件的派发策略和客户端接收响应结果逻辑一样,这里不再赘述。
将接收到的消息分发到线程池,线程池名称为:DubboServerHandler-10.204.246.187:20880-thread-。
提交给线程的任务是:ChannelEventRunnable
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { //获取处理线程 ExecutorService executor = getExecutorService(); try { executor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.RECEIVED, message)); } catch (Throwable t) { //提交线程失败,可以确定是线程池满了,需要将该提示响应给客户端 if(message instanceof Request && t instanceof RejectedExecutionException){ Request request = (Request)message; if(request.isTwoWay()){ String msg = "Server side(" + url.getIp() + "," + url.getPort() + ") threadpool is exhausted ,detail msg:" + t.getMessage(); Response response = new Response(request.getId(), request.getVersion()); response.setStatus(Response.SERVER_THREADPOOL_EXHAUSTED_ERROR); response.setErrorMessage(msg); channel.send(response); return; } } throw new ExecutionException(message, channel, getClass() + " error when process received event .", t); } } 接下来的逻辑则是利用线程池去针对请求做了异步处理
6. ChannelEventRunnable.run
处理不同状态的请求,仅仅只是一个中转,针对不同状态交给指定的方法处理。
RECEIVED、CONNECTED、DISCONNECTED、SENT、CAUGHT这里我们关注RECEIVED的处理链路。
public class ChannelEventRunnable implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { if (state == ChannelState.RECEIVED) { handler.received(channel, message); } else { switch (state) { case CONNECTED: handler.connected(channel); break; case DISCONNECTED: try { handler.disconnected(channel); break; case SENT: handler.sent(channel, message); break; case CAUGHT: handler.caught(channel, exception); break; default: } } }} 7. DecodeHandler.received
这里的解码主要是针对message对象是Decodeable对象的处理。前面以及解码为Request对象了,因此这里不会执行任何逻辑。
解码之后继续执行下一个handler的receive方法。
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { if (message instanceof Decodeable) { decode(message); } if (message instanceof Request) { decode(((Request) message).getData()); } if (message instanceof Response) { decode(((Response) message).getResult()); } handler.received(channel, message); } 8. HeaderExchangeHandler.received
处理Request请求,并异步返回Response,这里也是provider返回响应的入口
该方法分3个过程来看:
1、分请求类型进行处理:根据messgage的类型做不同的处理,例如正常的Request请求、Resopnse、telnet命令请求。
2、处理Request:继续向后执行(交给DubboProtocol的reply),得到异步调用结果。
3、返回Response: 将Request的调用id封装到Response,然后利用异步回调将结果封装到 Response 对象中,同时利用channel.send(res)方法将该结果发送给客户端(关于发送响应结果的过程会在下个部分进行分析);
@Override public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { //设置时间戳 channel.setAttribute(KEY_READ_TIMESTAMP, System.currentTimeMillis()); //获取通道 final ExchangeChannel exchangeChannel = HeaderExchangeChannel.getOrAddChannel(channel); try { if (message instanceof Request) { // handle request. Request request = (Request) message; // 处理事件 if (request.isEvent()) { handlerEvent(channel, request); } else { // 双向通信 if (request.isTwoWay()) { handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request); } else { //如果是单向通信,仅向后调用指定服务即可,无需返回调用结果 handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData()); } } } else if (message instanceof Response) { handleResponse(channel, (Response) message); } else if (message instanceof String) { if (isClientSide(channel)) { Exception e = new Exception("Dubbo client can not supported string message: " + message + " in channel: " + channel + ", url: " + channel.getUrl()); logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } else { String echo = handler.telnet(channel, (String) message); if (echo != null && echo.length() > 0) { channel.send(echo); } } } else { handler.received(exchangeChannel, message); } } finally { HeaderExchangeChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(channel); } } //处理请求 void handleRequest(final ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException { //封装resopnse(把requests的id封装到resopnse了) Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion()); //如果请求被破坏了, 响应异常 if (req.isBroken()) { ... ... res.setErrorMessage("Fail to decode request due to: " + msg); res.setStatus(Response.BAD_REQUEST); channel.send(res); return; } // 正常,取得请求数据,也就是 RpcInvocation 对象 Object msg = req.getData(); try { //继续向下调用 返回一个future CompletionStage 9. DubboProtocol.requestHandler.reply
1、获取invoker;
关于获取invoker主要过程是:- 取得serivce对应的key
- 根据key从exporterMap中获取对应的Export对象
- 通过export获取invoker
2、进入invoker调用链;
3、返回执行结果CompletableFuture;
public class DubboProtocol extends AbstractProtocol { private ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() { @Override public CompletableFuture Invoker getInvoker(Channel channel, Invocation inv) throws RemotingException { ... ... String serviceKey = serviceKey(port, path, inv.getAttachments().get(VERSION_KEY), inv.getAttachments().get(GROUP_KEY)); DubboExporter exporter = (DubboExporter ) exporterMap.get(serviceKey); if (exporter == null) { throw new RemotingException(channel, "Not found exported service: " + serviceKey + " in " + exporterMap.keySet() + ", may be version or group mismatch " + ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress() + ", message:" + inv); } return exporter.getInvoker(); } 服务端invoker调用链过程
这里大概梳理下调用链路:
ProtocolFilterWrapper.CallbackRegistrationInvoker.invoke ->EchoFilter.invoke ->ClassLoaderFilter.invoke ->GenericFilter.invoke ->ContextFilter.invoke ->TraceFilter.invoke ->TimeoutFilter.invoke ->MonitorFilter.invoke ->ExceptionFilter.invoke ->InvokerWrapper.invoke ->DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker.invoke ->AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke
关于经过的Filter这里不做说明,这里重点看下AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke方法:
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { try { //实际就是获取到代理类,然后调用对应的服务方法 Object value = doInvoke(proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments()); //把返回结果用CompletableFuture包裹 CompletableFuture 主要做了三件事情:
1. 获取代理类调用具体方法得到方法的返回;
2. 封装响应结果到CompletableFuture对象;
如果服务接口返回的就是CompletableFuture对象,则直接返回(),否则把服务接口同步返回的结果封装到CompletableFuture返回出去。
private CompletableFuture
3. 将上一步得到CompletableFuture对象,通过异步通知将结果封装成AsyncRpcResult返回出去。
到这里服务端处理客户请求过程分析完成,接下来看如何将上一步得到的Response响应给客户端。
这里我用一个时序图表示从HeaderExchangeHandler到服务接口最终执行的调用链路:
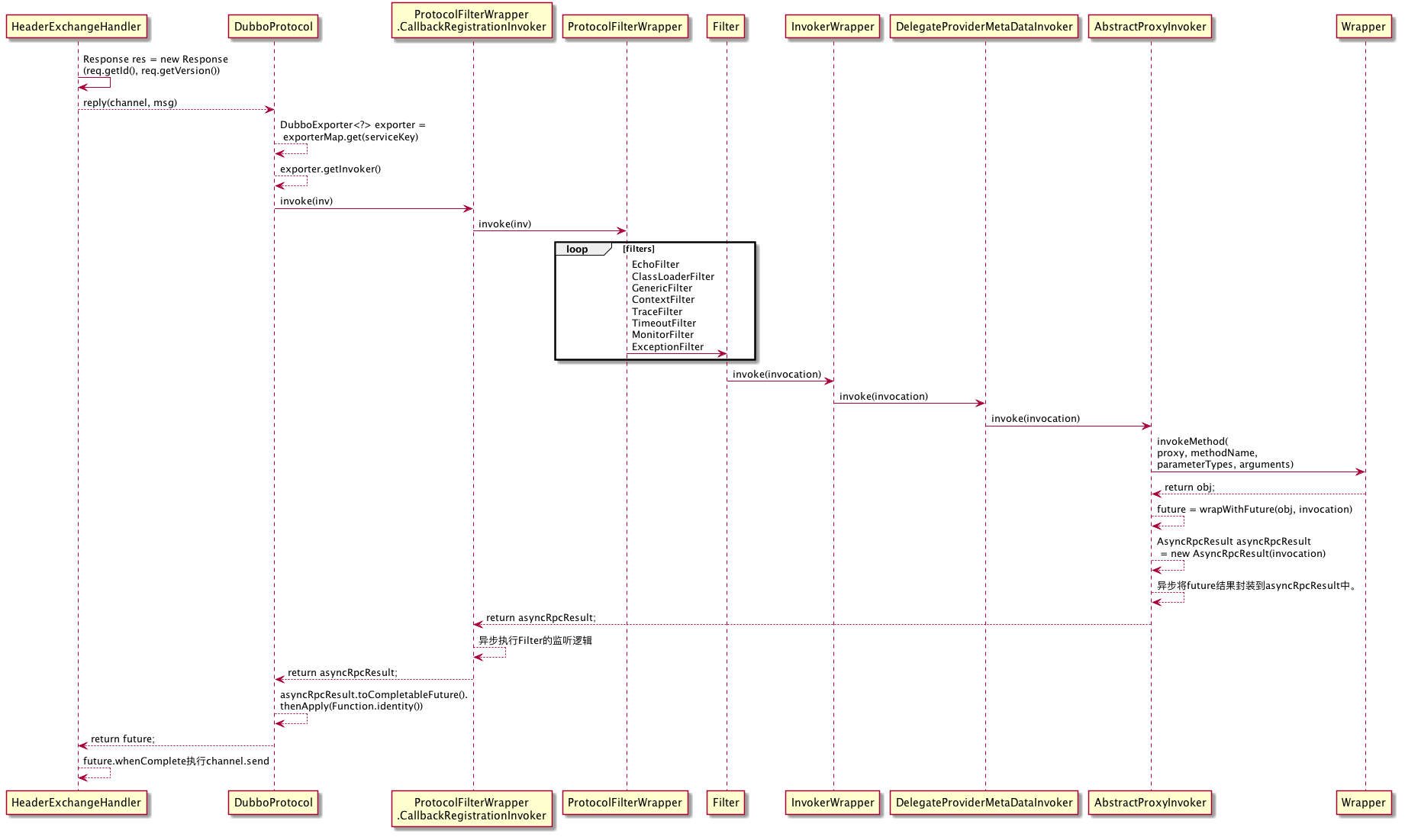
响应结果给客户端
在上一部分HeaderExchangeHandler.received的接收过程中,我们知道在得到结果后会将其发送给客户端,因此我们从HeaderExchangeChannel.send方法开始分析
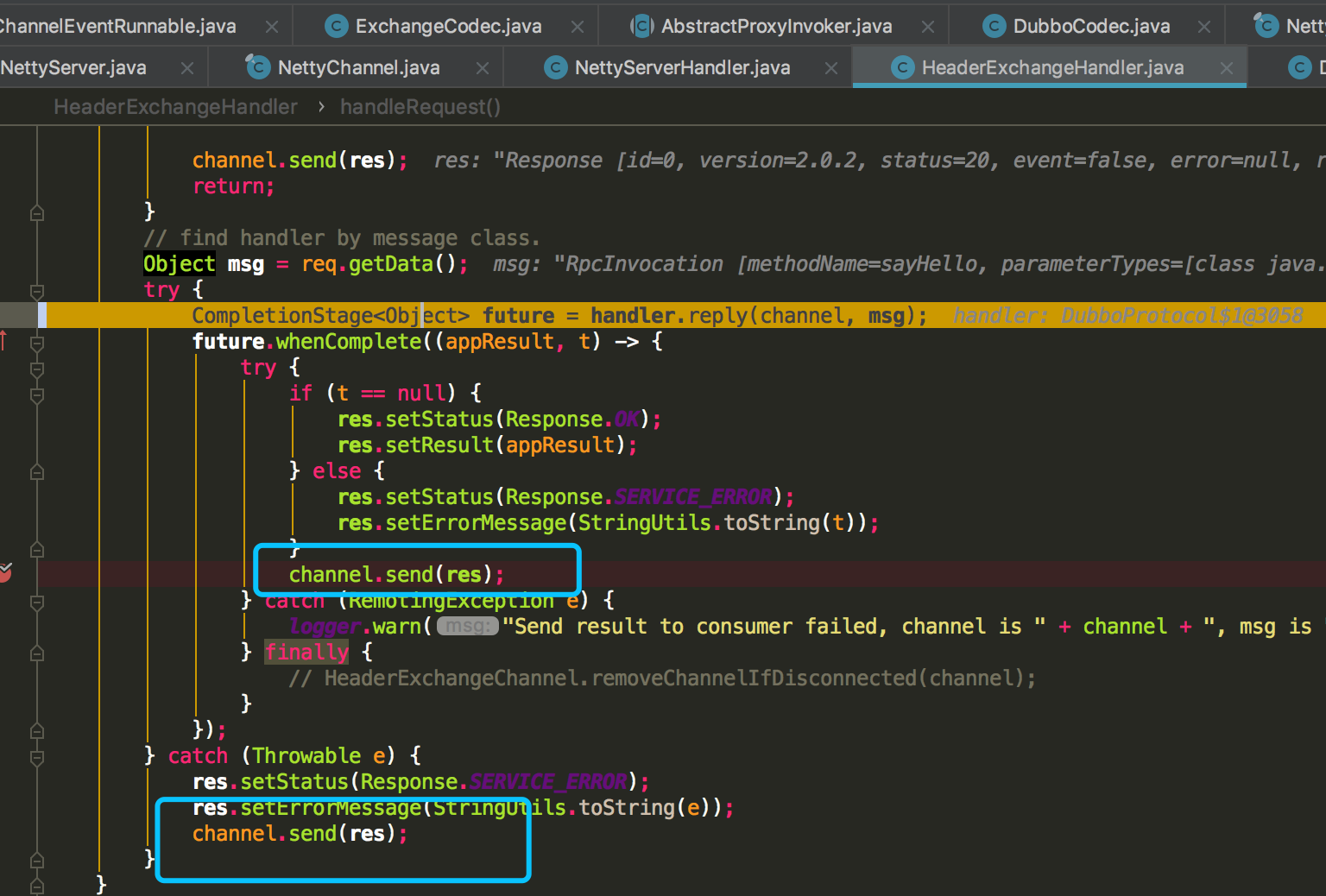
1. HeaderExchangeChannel.send
@Override public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException { if (closed) { throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send message " + message + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!"); } if (message instanceof Request || message instanceof Response || message instanceof String) { channel.send(message, sent); } else { Request request = new Request(); request.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion()); request.setTwoWay(false); request.setData(message); channel.send(request, sent); } } 2. NettyChannel.send
这里通过调用netty的api向channel中异步写入结果。
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException { // whether the channel is closed super.send(message, sent); boolean success = true; int timeout = 0; try { ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(message); if (sent) { // wait timeout ms timeout = getUrl().getPositiveParameter(TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT); success = future.await(timeout); } Throwable cause = future.cause(); if (cause != null) { throw cause; } } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + message + " to " + getRemoteAddress() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } if (!success) { throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + message + " to " + getRemoteAddress() + "in timeout(" + timeout + "ms) limit"); } } 接着则会经过NettyServerHandler的处理器以及编码器。NettyServerHandler.write方法将结果发送给客户端,后面的链路比较简单这里不做分析。
服务端的异步总结
1、首先服务端通过Netty接收到请求之后经过解码后派发给业务线程池(DubboServerHandler-ip:port-thread-)。这里是IO线程到业务线程的一次异步。
2、(如果服务接口返回的是CompletableFuture)则会异步将CompletableFuture的结果封装到AsyncRpcResult。
3、(如果服务接口返回的是CompletableFuture)AsyncRpcResult再异步执行channel.send();
4、channel.send()发送结果也是一次异步。
转载地址:http://obini.baihongyu.com/